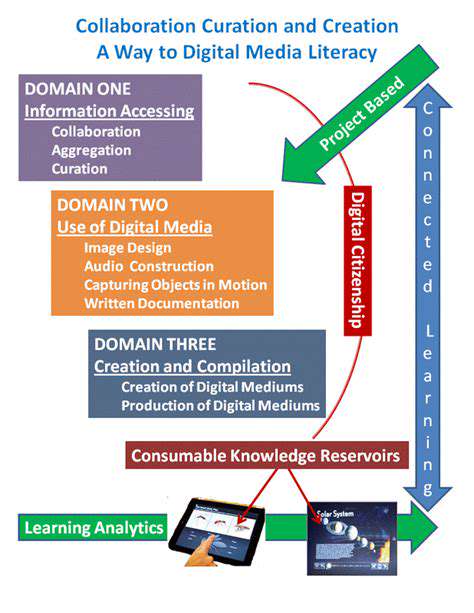
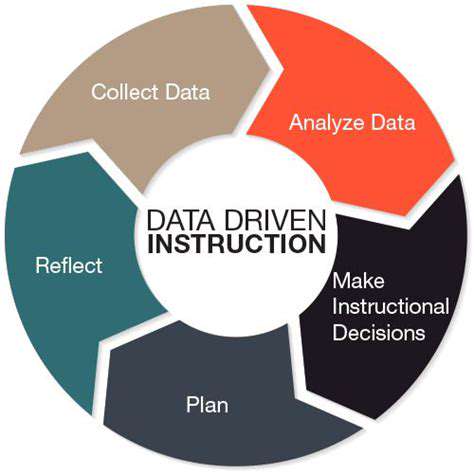
EdTech and the Future of Creative Industries

Augmented Reality: Enhancing the Real World
Augmented reality (AR) overlays digital information onto the user's real-world view, creating a blended experience. This technology is rapidly evolving and finding applications in diverse fields. AR overlays computer-generated sensory input, such as images, video, sound, or interactive elements, onto the user's perception of the real world. AR applications can range from simple overlays on smartphones to sophisticated systems used in industrial settings.
Imagine a construction worker using an AR app to visualize blueprints superimposed on a building site. This allows for real-time feedback, improved accuracy, and reduced errors in construction projects. AR is not just about entertainment; its practical applications are revolutionary and impactful.
Virtual Reality: Immersing in Simulated Worlds
Virtual reality (VR) creates entirely simulated environments. Users are immersed in these digital worlds, interacting with them as if they were physically present. VR systems commonly involve headsets, controllers, and other devices to create a fully immersive experience. The possibilities of VR are vast, extending from gaming and entertainment to training and education.
VR simulations offer a safe and controlled environment for training in high-risk situations. Imagine a surgeon practicing complex procedures in a VR operating room without the risks of real-life surgery. This is just one example of the transformative potential of VR in healthcare and other professional fields.
The Convergence of AR and VR
The lines between AR and VR are blurring, with the emergence of mixed reality (MR) experiences. MR combines elements of both, allowing users to interact with both the real and virtual world simultaneously. MR experiences are still evolving, but they promise to revolutionize how we interact with technology and the world around us.
Applications in Healthcare
Both AR and VR are finding significant applications in healthcare. AR can guide surgeons during procedures, providing real-time overlays of anatomical data. VR can simulate complex medical scenarios for training purposes, allowing medical professionals to practice in a safe and controlled environment. These technologies are poised to transform healthcare education and patient care.
Education and Training
AR and VR are transforming the way we learn and train. Interactive simulations in VR can immerse learners in historical events, scientific concepts, or complex procedures, making learning more engaging and effective. AR can overlay information onto real-world objects, providing contextual learning. The interactive nature of these technologies makes them ideal for immersive learning experiences.
Entertainment and Gaming
The gaming and entertainment industries have embraced AR and VR with open arms. VR gaming offers unparalleled immersion, transporting players into virtual worlds with incredible detail and interactivity. AR games enhance the real world with digital elements, blurring the lines between reality and fantasy. The development of sophisticated AR and VR experiences is changing the entertainment landscape, creating exciting new opportunities for interaction and engagement.
Microbial sensors represent a transformative advancement in environmental monitoring, offering a unique blend of sensitivity and speed in detecting pollutants. These systems leverage the inherent capabilities of microorganisms to respond to specific chemical or physical changes in their environment. This allows for rapid and real-time assessment of environmental quality, providing crucial data for effective pollution control and remediation strategies.


Read more about EdTech and the Future of Creative Industries
Hot Recommendations
- The Gamified Parent Teacher Conference: Engaging Stakeholders
- Gamification in Education: Making Learning Irresistibly Fun
- The Future of School Libraries: AI for Personalized Recommendations
- EdTech and the Future of Creative Industries
- Empowering Student Choice: The Core of Personalized Learning
- Building Community in a Hybrid Learning Setting
- VR for Special Education: Tailored Immersive Experiences
- Measuring the True Value of EdTech: Beyond Adoption Rates
- Addressing Digital Divide in AI Educational Access
- Preparing the Workforce for AI Integration in Their Careers