Mobile Learning for Digital Literacy Skills
Mobile Learning for Specific Digital Literacy Domains
Mobile Learning for Specific Digital Literacy Skills
Mobile learning provides a versatile and convenient way to build targeted digital literacy competencies. Learners interact with simulations, real-world tasks, and multimedia materials directly on their smartphones or tablets, creating tangible skill-building opportunities. This method proves especially valuable for teaching concrete abilities like evaluating online sources, producing multimedia content, and applying cybersecurity best practices. What sets mobile learning apart is its ability to customize both content delivery and practice exercises, meeting individual preferences and progress rates. Since mobile devices are nearly always within reach, this approach removes location barriers, making digital education available to wider audiences.
Modern mobile learning solutions frequently include game-like features that boost participation and knowledge retention. Progress tracking, achievement badges, and interactive scenarios turn skill development into an engaging journey rather than a chore. These motivational elements have been shown to increase both completion rates and long-term skill application, particularly for technical subjects like digital literacy.
Engaging Content for Diverse Learning Styles
Successful mobile learning initiatives for digital competency recognize that individuals process information differently. They incorporate video tutorials for visual learners, podcast-style explanations for auditory processors, and touch-screen interactions for hands-on learners. This multi-format approach doesn't just accommodate different preferences - it actively reinforces learning through multiple neural pathways. Research indicates that material presented in multiple formats leads to 40% better retention compared to single-format delivery.
Intelligent learning systems now analyze user interactions to dynamically adjust content difficulty and presentation style. If a learner struggles with text-based cybersecurity concepts, the platform might automatically offer an animated explainer or interactive scenario. This responsive approach helps prevent frustration while ensuring all students achieve competency regardless of their starting point.
Accessibility and Inclusivity in Mobile Learning
Truly effective digital literacy programs consider the full spectrum of user needs. This means offering content in multiple languages, ensuring compatibility with both premium and budget devices, and implementing robust accessibility features. Digital inclusion isn't optional - it's a fundamental requirement for equitable education in the 21st century. Features like voice control, high-contrast modes, and closed captioning transform mobile learning from a privilege to a right for learners with visual, auditory, or motor impairments.
Collaborative features in mobile learning apps create virtual classrooms without walls. Discussion forums moderated by educators allow safe peer-to-peer knowledge sharing, while group projects facilitate practical application of digital skills. These social learning components mirror real-world digital collaboration, preparing learners for professional environments where digital teamwork is expected.
Practical Application and Real-World Scenarios
The most impactful mobile learning connects theoretical knowledge to concrete situations learners actually encounter. Instead of abstract cybersecurity rules, students might analyze actual phishing attempts from their own inboxes. Rather than hypothetical social media guidelines, they create and refine actual online profiles with privacy settings. This applied learning approach bridges the gap between knowing concepts and using them competently. Assessment shifts from memorization tests to portfolio reviews where learners demonstrate practical digital capabilities.
Authentic application projects might include creating a personal website with proper accessibility features, producing a video tutorial explaining a digital concept to peers, or conducting an online research project with proper citation methods. These tangible outcomes give learners confidence in their digital abilities while creating assets they can use in academic or professional contexts.
Future Trends and Opportunities in Mobile Digital Literacy
Mobile Learning Platforms and Personalized Learning
The next generation of digital literacy education leverages adaptive algorithms that customize learning paths in real-time. These systems don't just adjust content difficulty - they identify each learner's optimal modality (visual, auditory, kinesthetic) and time of peak alertness. Some experimental platforms even modify content based on biometric feedback from wearable devices, slowing pace when stress levels rise or offering breaks when attention wanes.
Artificial intelligence now provides what even the most attentive human instructor cannot - instantaneous, personalized feedback at scale. Machine learning algorithms detect subtle patterns in error types, predicting which concepts will challenge a learner before they encounter them. This allows for preemptive reinforcement, creating smoother learning curves and reducing frustration. The resulting analytics give educators unprecedented insight into class-wide competency gaps.
Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality Integration
Emerging AR applications transform everyday environments into digital literacy laboratories. A smartphone camera might overlay network security indicators on a public WiFi hotspot, or highlight suspicious elements in a simulated phishing email. VR environments allow safe experimentation with advanced digital tools - practicing website development in a virtual coding studio or testing cybersecurity responses in simulated breach scenarios.
These immersive technologies excel at teaching abstract digital concepts through concrete experiences. Network security principles become tangible when students visually trace data packets through virtual networks, watching encryption protocols activate. Spatial computing allows learners to physically manipulate digital security concepts, building intuitive understanding that transfers to real-world application.
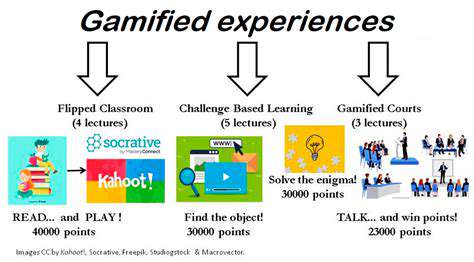
Gamification and Interactive Learning Activities
Next-level gamification moves beyond superficial badges to create rich narrative experiences. Digital literacy becomes an adventure where learners progress by mastering real competencies - unlocking encryption tools to solve storyline challenges or building secure networks to protect virtual communities. These narrative frameworks provide context that makes technical skills feel purposeful and relevant.
The most effective interactive activities mirror professional digital workflows. Learners might conduct simulated cybersecurity audits, troubleshoot realistic system failures, or collaborate on time-sensitive digital projects. These pressure-tested experiences build both skill and confidence, ensuring learners can perform when it matters rather than just during controlled assessments.
Read more about Mobile Learning for Digital Literacy Skills
Hot Recommendations
- The Gamified Parent Teacher Conference: Engaging Stakeholders
- Gamification in Education: Making Learning Irresistibly Fun
- The Future of School Libraries: AI for Personalized Recommendations
- EdTech and the Future of Creative Industries
- Empowering Student Choice: The Core of Personalized Learning
- Building Community in a Hybrid Learning Setting
- VR for Special Education: Tailored Immersive Experiences
- Measuring the True Value of EdTech: Beyond Adoption Rates
- Addressing Digital Divide in AI Educational Access
- Preparing the Workforce for AI Integration in Their Careers