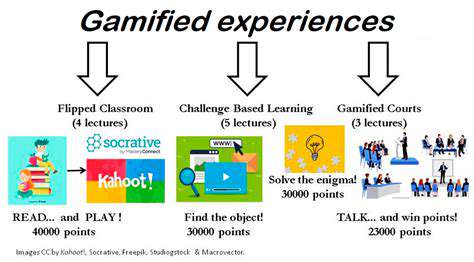
Beyond Badges: Designing Meaningful Gamified Experiences
Leveraging the Power of Autonomy
True autonomy in design extends far beyond superficial choices. It requires creating systems where users feel genuine ownership over their experience. This might involve customizable interfaces, branching narrative paths, or user-generated content features. The key lies in making participants feel their decisions meaningfully shape their journey rather than simply selecting from predetermined options.
Authentic autonomy manifests when systems demonstrate responsiveness to user input. This could include dynamic environments that evolve based on player behavior or feedback mechanisms that visibly incorporate user suggestions. When participants see their choices directly influence the experience, their intrinsic engagement deepens substantially.
Cultivating a Sense of Mastery
Effective mastery systems balance challenge and skill development through carefully calibrated progression curves. These should provide:
- Clear indicators of progress (skill trees, achievement milestones)
- Gradually increasing complexity that matches developing competencies
- Constructive feedback that highlights both strengths and areas for growth
This approach transforms the learning process into an engaging journey where each accomplishment fuels motivation for the next challenge.
Creating Meaningful Goals and Purpose
Purpose-driven design connects individual actions to larger narratives or community impacts. This might involve:
- Storylines that contextualize tasks within compelling scenarios
- Visualizations showing collective progress toward shared objectives
- Mechanisms that demonstrate real-world impact of in-system actions
When participants see how their contributions fit into something larger, their engagement transcends superficial participation.
Designing for Social Connection
Social features should facilitate authentic interactions rather than superficial competition. Consider:
- Collaborative problem-solving scenarios
- Knowledge-sharing systems
- Community recognition mechanisms
These approaches foster genuine connections that reinforce intrinsic motivation through shared purpose and mutual support.
Balancing Extrinsic and Intrinsic Rewards
The most effective systems use extrinsic rewards as milestones that highlight intrinsic achievements rather than substitutes for genuine engagement. Badges and points work best when they serve as recognition of mastery rather than the primary motivation for participation. This subtle but crucial distinction maintains the integrity of the intrinsic motivation while providing visible markers of progress.
Creating Meaningful Challenges and Feedback Loops
Designing Engaging Activities
Well-crafted activities in educational contexts should strike a balance between enjoyment and cognitive stimulation. The most effective designs incorporate elements that naturally align with human curiosity and problem-solving instincts. Rather than relying on artificial gamification layers, these activities should integrate challenge and reward organically within the learning context.
Activity design benefits tremendously from iterative testing with representative user groups. This process reveals:
- Natural engagement patterns
- Unanticipated pain points
- Emergent creative uses
Such insights allow for refinements that enhance intrinsic motivation while maintaining educational integrity.
Defining Clear Objectives
Objective-setting represents a crucial design challenge - how to provide direction without stifling creativity. Effective objectives should:
- Establish clear parameters for success
- Allow multiple pathways to achievement
- Scale appropriately for different skill levels
This framework provides necessary structure while preserving the autonomy that fuels intrinsic motivation.
Establishing Realistic Expectations
Expectation management requires careful calibration of:
- Challenge difficulty curves
- Time investment requirements
- Skill development trajectories
Transparent communication about these elements prevents frustration while maintaining engagement. Well-designed systems provide adaptive challenges that automatically adjust to individual capability levels.
Encouraging Collaboration and Communication
Collaboration systems work best when they:
- Highlight complementary skills
- Provide tools for knowledge sharing
- Recognize group achievements
These features transform social interaction from a peripheral element to a core motivational driver.
Evaluating Progress and Providing Feedback
Effective feedback systems should:
- Highlight specific achievements
- Suggest targeted improvements
- Provide resources for skill development
This approach transforms feedback from evaluation to empowerment, maintaining motivation through the learning process.
Measuring Impact Beyond Metrics

Understanding the Limitations of Traditional Metrics
While quantitative measures provide valuable benchmarking data, they often fail to capture the nuanced human experiences that define true impact. An overreliance on easily measurable outputs can create distorted perceptions of program effectiveness. For example, participant counts reveal nothing about engagement depth, while completion rates don't reflect learning retention or behavioral changes.
Considering Qualitative Data for a More Holistic View
Rich qualitative data emerges through:
- In-depth participant interviews
- Observational studies
- Longitudinal case studies
These methods reveal the transformative potential that numbers alone cannot convey. They capture emotional responses, unexpected outcomes, and subtle behavioral shifts that collectively define real impact.
Developing a Framework for Comprehensive Impact Assessment
A robust assessment framework integrates:
| Data Type | Collection Method | Analysis Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Quantitative | Surveys, usage analytics | Statistical analysis |
| Qualitative | Interviews, observations | Thematic analysis |
This blended approach provides both measurable outcomes and contextual understanding.
Identifying Key Stakeholders and Their Needs
Impact assessment requires mapping:
- Primary beneficiaries
- Secondary stakeholders
- Institutional partners
Each group maintains distinct success criteria that must inform the evaluation process. This stakeholder-centric approach ensures relevance across all levels of analysis.
Implementing and Tracking Progress Towards Goals
Effective implementation involves:
- Regular progress reviews
- Adaptive strategy adjustments
- Transparent reporting mechanisms
This cyclical process ensures continuous alignment between activities and intended impacts. It transforms evaluation from a static endpoint into an ongoing improvement mechanism.