Accessibility in Immersive Learning: Designing for All Users
Catering to Varying Learning Styles
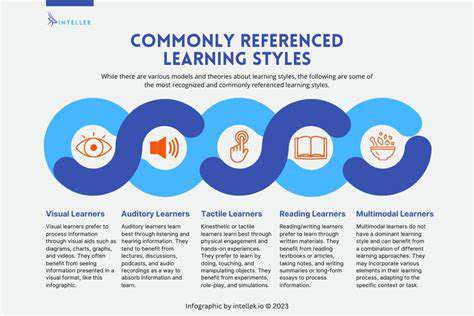
Immersive learning environments, with their dynamic and engaging nature, offer a powerful tool for diverse learners. However, effective implementation requires careful consideration of individual learning preferences. Students who thrive on visual stimulation may benefit from interactive 3D models and simulations, while auditory learners might find audio narratives and sound design more engaging. A truly accessible immersive learning experience acknowledges these differences and provides multiple avenues for knowledge acquisition, ensuring that the medium supports, rather than hinders, individual learning styles.
Recognizing and accommodating kinesthetic learning is also crucial. Immersive environments can incorporate interactive elements that allow learners to manipulate virtual objects, experiment with different scenarios, and build their understanding through hands-on experience. This approach not only enhances engagement but also fosters a deeper understanding of the material by connecting theory to practical application.
Visual Impairments and Accessibility
Accessibility for individuals with visual impairments is paramount in immersive learning. Screen readers and alternative text descriptions are essential components for navigating virtual environments and accessing content. Utilizing high contrast color schemes and providing text-based options for visual elements are also critical. These adjustments ensure that students with visual impairments can fully participate and benefit from the immersive experience, avoiding exclusion and promoting equal opportunity.
Providing alternative methods for visual navigation and interaction, such as audio cues and tactile feedback, further enhances accessibility. These features can significantly improve the learning experience for individuals with visual impairments, transforming immersive learning into an inclusive environment.
Auditory Impairments and Adaptations
Similarly, learners with auditory impairments necessitate adaptations in immersive learning. Captions and transcripts for audio elements are crucial for understanding dialogue and environmental sounds. Using visual cues, animations, or alternative methods of communication can also aid comprehension. These accommodations ensure learners with auditory impairments can follow along and process information without experiencing any barriers to understanding.
Furthermore, providing adjustable volume levels and the ability to mute or turn off distracting sounds are critical for creating a supportive and inclusive environment. Such adjustments allow learners with auditory sensitivities to personalize their learning experience and focus on the material without discomfort.
Cognitive Diversity and Personalized Learning
Immersive learning platforms can be customized to address the specific needs of learners with cognitive differences. Features such as adjustable pacing, simplified interfaces, and interactive guides that break down complex information into smaller, manageable chunks can be invaluable for learners with varying cognitive abilities.
Personalized learning paths that adapt to individual learner progress and strengths are crucial. By allowing learners to navigate at their own pace, access targeted support, and focus on areas requiring additional attention, immersive learning becomes a powerful tool for inclusivity and personalized development.
Motor Disabilities and Adapted Controls
Students with motor disabilities require accessible controls and interactions within immersive environments. Offering alternative input methods, such as voice commands, eye-tracking technology, or customized controller options, ensures inclusivity. These adaptations allow learners to interact with the virtual world in a manner that accommodates their specific needs and abilities. This inclusivity promotes equal access and prevents exclusion.
Furthermore, assistive technologies integrated seamlessly into the immersive environment can significantly enhance the learning experience for learners with motor impairments. Such tools provide the necessary support to ensure full participation and maximize learning outcomes.
Cultural Sensitivity and Representation
A truly inclusive immersive learning environment should reflect the diversity of the world around us. Representing a wide range of cultures, backgrounds, and perspectives within the virtual environment is crucial. This representation fosters understanding and respect for various cultures and identities, creating a welcoming and inclusive space for all learners. The virtual world should be a mirror that reflects the diverse tapestry of human experience and not a sterile echo chamber.
Incorporating diverse voices, perspectives, and cultural contexts within the immersive content is vital. Stories, characters, and scenarios that represent a wide range of experiences promote empathy, understanding, and tolerance among learners, fostering a sense of belonging and promoting a global perspective.

Pedagogical Strategies for Inclusive Learning
Differentiated Instruction for Diverse Learners
Implementing pedagogical strategies that cater to diverse learning styles and needs is crucial for inclusive learning. Differentiated instruction, which tailors teaching methods, materials, and assessments to individual student needs, is a key component. This involves recognizing that learners possess varying strengths, weaknesses, and paces of learning. Adjustments might include providing different levels of support, utilizing varied instructional materials (visual aids, hands-on activities, audio recordings), and offering multiple avenues for demonstrating understanding (projects, presentations, written assignments). This approach acknowledges that one-size-fits-all instruction is ineffective in fostering the growth of all students.
Moreover, differentiated instruction necessitates ongoing assessment and adaptation. Teachers must regularly gather information about student learning through various methods, such as observation, questioning, and formative assessments. Based on this data, educators can make informed decisions about adjusting their instructional strategies to better meet the specific needs of their students. This iterative process of assessment, adaptation, and refinement ensures that learning experiences are optimally tailored to each learner's unique profile.
Utilizing Universal Design for Learning (UDL) Principles
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) provides a framework for creating inclusive learning environments that cater to the diverse needs of all learners. UDL principles emphasize flexibility in the presentation of content, the provision of multiple means of representation, action and expression, and engagement. By incorporating UDL principles in immersive learning experiences, educators can ensure that all students have the opportunity to access and participate fully.
UDL strategies in immersive environments often involve utilizing various input modalities. For example, providing transcripts of audio components, offering alternative text descriptions for images, and offering multiple ways to interact with virtual environments. These accommodations ensure that students with diverse needs, such as visual impairments, auditory processing differences, or motor skill limitations, can actively participate in the learning experience.
Additionally, UDL principles encourage the use of varied assessment methods. This means moving beyond traditional tests and incorporating alternative methods such as projects, presentations, and portfolios. This approach recognizes that different learners may excel in different areas and allows for a more comprehensive evaluation of their understanding and skills.
By embracing UDL principles, educators can create immersive learning experiences that are accessible and engaging for all students, fostering a sense of belonging and promoting their overall success.
Collaborative Learning and Peer Support
Collaborative learning activities can significantly enhance the inclusive nature of immersive learning environments. By creating opportunities for students to work together, share ideas, and support one another, educators foster a sense of community and mutual understanding. Collaborative projects in virtual environments can allow students to leverage each other's strengths, learn from diverse perspectives, and develop essential social and communication skills.
Peer support plays a vital role in fostering inclusivity. Encouraging peer mentoring or buddy systems can provide valuable support and guidance to learners who might require additional assistance. This approach not only empowers learners but also builds a supportive and inclusive learning community where everyone feels valued and respected.
Furthermore, incorporating opportunities for peer feedback and constructive criticism in collaborative tasks can enhance the learning experience for all. This process fosters a culture of mutual respect and helps students refine their skills and knowledge in a supportive environment. By embracing collaborative learning and peer support, educators can cultivate a dynamic and inclusive learning space where students feel empowered to learn from and with each other.
Measuring and Evaluating Accessibility in Immersive Learning
Understanding the Need for Accessibility in Immersive Learning
Immersive learning environments, leveraging technologies like virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), offer exciting potential for engaging students. However, the accessibility of these experiences is crucial to ensure equitable participation and learning outcomes for all. Failing to consider accessibility can create significant barriers for students with disabilities, preventing them from fully benefiting from the educational opportunities these technologies offer. This necessitates a proactive and comprehensive approach to accessibility assessment and improvement.
Accessibility in immersive learning encompasses a wide range of factors, from the design of the virtual environment itself to the provision of alternative input and output methods. This includes considerations for users with visual, auditory, motor, and cognitive impairments, ensuring that the experience is inclusive and accessible to everyone.
Defining Accessibility Criteria for Immersive Experiences
Establishing clear accessibility criteria is essential for evaluating the effectiveness of immersive learning environments. These criteria should address the specific needs of diverse learners, encompassing aspects like adjustable lighting, color contrast, and text size within the virtual space. These criteria must also consider alternative navigation methods, providing options for users with limited dexterity or mobility issues.
Furthermore, the criteria should include considerations for audio descriptions, transcripts, and captions for auditory content, ensuring that all learners can access and comprehend the information presented.
Methods for Measuring Visual Accessibility
Evaluating visual accessibility in immersive learning environments requires careful attention to the design elements within the virtual world. This includes analyzing the color contrast ratios between elements, ensuring sufficient luminance levels, and assessing the overall visual clarity of the experience. Thorough testing should involve users with varying visual impairments to identify and address potential issues.
Assessing Auditory Accessibility in Immersive Environments
Auditory accessibility is equally important in immersive learning. Evaluations should include analyzing the volume levels of audio cues, the clarity of spoken content, and the presence of captions or transcripts. Considerations must also include the potential for background noise interference and the provision of alternative audio options for learners with auditory processing difficulties.
Evaluating the Usability of Alternative Input Methods
The usability of alternative input methods, such as voice commands, assistive touchpads, and customized controllers, is critical for accessibility. Comprehensive testing should involve users with various motor impairments to identify any usability challenges or limitations. The effectiveness of these alternative methods in facilitating navigation and interaction within the immersive environment needs careful consideration and evaluation.
Implementing and Monitoring Accessibility Features
Integrating accessibility features into immersive learning environments requires a multifaceted approach. This includes incorporating user feedback, conducting periodic reviews, and implementing ongoing monitoring mechanisms to ensure continued compliance with accessibility standards. Regular updates and improvements based on user feedback are essential to maintain the accessibility of these innovative learning tools.
Effective evaluation and implementation of accessibility features in immersive learning environments is paramount to ensuring that all learners have equal access to high-quality educational experiences, regardless of their abilities.
Read more about Accessibility in Immersive Learning: Designing for All Users
Hot Recommendations
- The Gamified Parent Teacher Conference: Engaging Stakeholders
- Gamification in Education: Making Learning Irresistibly Fun
- The Future of School Libraries: AI for Personalized Recommendations
- EdTech and the Future of Creative Industries
- Empowering Student Choice: The Core of Personalized Learning
- Building Community in a Hybrid Learning Setting
- VR for Special Education: Tailored Immersive Experiences
- Measuring the True Value of EdTech: Beyond Adoption Rates
- Addressing Digital Divide in AI Educational Access
- Preparing the Workforce for AI Integration in Their Careers