The Evolution of Assessment Design: Beyond Standardized Tests
The Limitations of Traditional Standardized Tests
Traditional Stagnation in the Modern Economy
Traditional stagnation, a persistent period of slow economic growth, can stem from various factors, including technological stagnation and insufficient investment in human capital. This can lead to widespread economic hardship and reduced opportunities for individuals and communities. Understanding the root causes of such stagnation is crucial to developing effective solutions.
While periods of slow growth can occur naturally, prolonged stagnation can signify deeper underlying issues. These could include a lack of innovation, an inflexible regulatory environment, or an inadequate infrastructure to support economic expansion. Addressing these issues requires a multifaceted approach that considers both short-term and long-term strategies.
Technological Limitations and Innovation
Traditional economic models often fail to account for the rapid pace of technological advancement. The limitations of existing technologies can hinder productivity gains and limit the potential for economic growth. A lack of investment in research and development can lead to a shortfall in innovation, further perpetuating the stagnation.
The gap between technological possibilities and their practical application can be a significant barrier to economic progress. This requires a concerted effort to bridge the gap between theoretical advancements and their implementation in the real world to drive innovation and growth.
Insufficient Investment in Human Capital
A skilled and educated workforce is a cornerstone of a thriving economy. Insufficient investment in education and training programs can lead to a shortage of skilled workers, hindering productivity and economic growth. The resulting workforce may lack the necessary skills to compete in the global marketplace.
Structural Issues and Regulations
Outdated regulations and structural impediments can significantly hinder economic growth. Complex and bureaucratic regulations can stifle entrepreneurship and investment, leading to a decrease in overall productivity and economic activity. These regulations can create an environment that discourages innovation and discourages investment in new ventures.
Moreover, inefficient governance structures and corruption can further exacerbate these challenges and impede the development of a robust and resilient economy.
Market Failures and External Shocks
Market failures, such as information asymmetry and externalities, can lead to inefficient resource allocation and hinder overall economic development. These market failures can result in a misallocation of resources, which can impede economic growth and create instability.
External shocks, such as global economic crises or natural disasters, can also disrupt economic activity and create a period of stagnation. Responding effectively to these shocks requires robust economic policies and a resilient infrastructure.
Embracing Alternative Assessment Strategies

Exploring the Benefits of Alternative Assessments
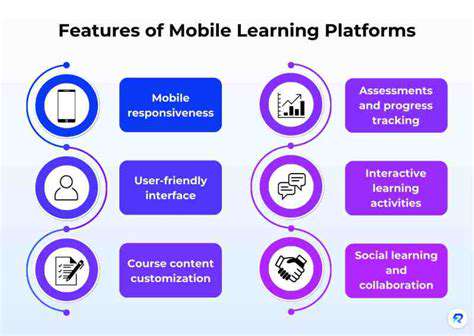
Alternative assessments offer a more comprehensive understanding of student learning by moving beyond traditional methods like multiple-choice tests. These assessments can reveal a deeper understanding of a student's abilities, allowing teachers to identify strengths and weaknesses more effectively. They also provide a more engaging learning experience for students, fostering a greater appreciation for the subject matter. By incorporating these methods, educators can tailor their teaching strategies to better meet individual student needs.
One of the key advantages of alternative assessments is their ability to measure higher-order thinking skills. These skills, such as critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity, are often overlooked in traditional assessments, but are crucial for success in today's world. Alternative assessments can effectively evaluate these skills through projects, presentations, portfolios, and other hands-on activities.
Catering to Diverse Learning Styles
Alternative assessment methods cater to a wide range of learning styles, from visual learners who thrive on presentations and diagrams to kinesthetic learners who benefit from hands-on projects. This personalized approach allows students to demonstrate their understanding in ways that best suit their individual preferences and strengths.
By embracing alternative assessments, educators can create a more inclusive learning environment where every student feels valued and empowered to showcase their knowledge and skills. This inclusivity fosters a more positive and productive learning experience for all students.
Enhancing Student Engagement and Motivation
Students are often more engaged and motivated when they are given opportunities to demonstrate their knowledge and skills in creative and meaningful ways. Alternative assessments, such as creating a presentation, designing a project, or developing a portfolio, can significantly enhance student interest and participation.
These methods encourage active learning and provide students with a sense of ownership over their learning process. This, in turn, can lead to increased motivation and a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Promoting Deeper Understanding and Critical Thinking
Assessment methods that move beyond rote memorization and focus on higher-order thinking skills promote a deeper understanding of concepts. Students are challenged to analyze, evaluate, and synthesize information, which leads to a more robust comprehension of the subject matter.
Facilitating Personalized Learning Experiences
Alternative assessments provide valuable insights into each student's unique learning style, strengths, and weaknesses. This information allows teachers to tailor instruction and support to meet individual needs, resulting in more effective and engaging learning experiences.
By understanding individual learning styles and preferences, teachers can create a more personalized learning environment where students feel supported and challenged to reach their full potential.
Improving Feedback and Communication
Alternative assessments provide opportunities for more detailed and constructive feedback. Instead of simply grading a test, teachers can provide specific and actionable suggestions for improvement based on the student's performance on projects, presentations, or portfolios. This personalized feedback can significantly benefit students' learning process.
This allows for a more meaningful dialogue between the teacher and the student, fostering a stronger relationship based on mutual understanding and support. This is crucial for student growth and success.
The Power of Formative Assessment

Understanding Formative Assessment
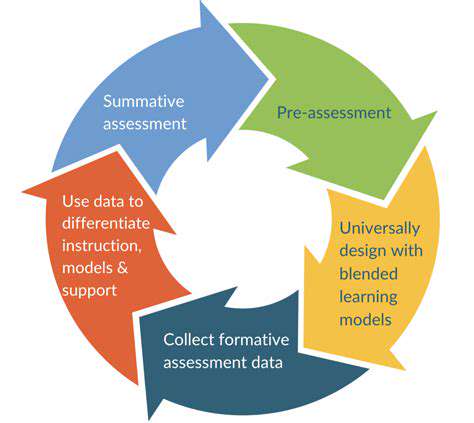
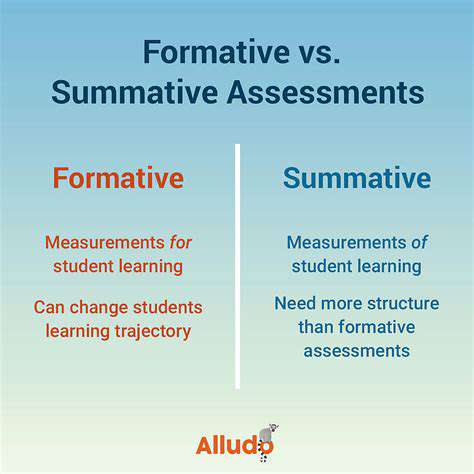
Formative assessment is a crucial component of effective teaching and learning. It's not about evaluating students for a grade, but rather about gathering information to adjust instruction and support student growth. This process allows educators to identify areas where students are struggling and adapt their teaching methods accordingly, ensuring that all students have the opportunity to succeed. Formative assessments are ongoing and provide immediate feedback, allowing for timely interventions and adjustments. By understanding student needs in real-time, teachers can tailor their lessons to meet those needs, fostering a more dynamic and effective learning environment.
The ultimate goal of formative assessment is to enhance learning and improve student outcomes. It's a continuous cycle of gathering information, analyzing it, and using that information to improve instruction. This approach is particularly valuable in identifying gaps in knowledge and skills, enabling teachers to provide targeted support and resources.
Types of Formative Assessment Methods
There are various methods for conducting formative assessment, ranging from simple observations to more structured activities. Quick quizzes, exit tickets, think-pair-share discussions, and informal questioning are all effective tools for gathering real-time feedback. These methods allow teachers to understand students' current understanding and identify areas requiring further clarification.
Observations of student work during class activities or projects provide valuable insights into individual learning styles and challenges. This direct observation can often reveal patterns and misconceptions that might not be apparent through traditional assessment methods.
Benefits of Implementing Formative Assessment
Implementing formative assessment strategies offers a wealth of benefits for both students and teachers. It fosters a growth mindset by encouraging students to reflect on their learning and identify areas for improvement. This focus on improvement, rather than just grades, empowers students to take ownership of their learning journey.
For teachers, formative assessment provides invaluable data that informs instructional decisions. This data allows teachers to adjust their teaching strategies, ensuring that lessons are relevant and engaging for all students. This data-driven approach to teaching enhances the overall quality of instruction.
Strategies for Effective Formative Assessment
To maximize the effectiveness of formative assessment, teachers should develop clear learning objectives and align assessment tasks with these objectives. This ensures that the assessment accurately measures students' understanding of the targeted concepts. This alignment helps in streamlining the process and ensuring that the assessment truly reflects the learning goals.
Integrating Formative Assessment into the Curriculum
Integrating formative assessment into the curriculum should be a seamless process, not an additional burden. Teachers can incorporate these strategies into daily lessons, making them an integral part of the learning experience. By embedding formative assessment into the lesson flow, teachers can gather feedback in a natural and unobtrusive manner.
A well-structured and thoughtful implementation of formative assessment can greatly enhance the learning experience for both students and teachers. By actively incorporating these methods, teachers can create a more dynamic and supportive learning environment that fosters student success.
Assessment Tools and Technology
Various tools and technologies can support the implementation of formative assessment. Online quizzes, interactive whiteboards, and digital portfolios can provide immediate feedback and facilitate data analysis. These tools make it easier for teachers to track student progress and identify areas that require further attention. Utilizing these digital resources can streamline the data collection and analysis process, allowing teachers to focus more on providing targeted support to their students.
Digital tools and resources can often create a more engaging and interactive learning environment. This can encourage student participation and foster a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Read more about The Evolution of Assessment Design: Beyond Standardized Tests
Hot Recommendations
- The Gamified Parent Teacher Conference: Engaging Stakeholders
- Gamification in Education: Making Learning Irresistibly Fun
- The Future of School Libraries: AI for Personalized Recommendations
- EdTech and the Future of Creative Industries
- Empowering Student Choice: The Core of Personalized Learning
- Building Community in a Hybrid Learning Setting
- VR for Special Education: Tailored Immersive Experiences
- Measuring the True Value of EdTech: Beyond Adoption Rates
- Addressing Digital Divide in AI Educational Access
- Preparing the Workforce for AI Integration in Their Careers