Measuring Cognitive Outcomes in Personalized Learning Environments
Introduction to Personalized Learning and Assessment

Understanding the Core Concept
Personalized learning, at its heart, is a pedagogical approach that tailors educational experiences to meet the unique needs, interests, and learning styles of each individual student. This approach recognizes that students don't all learn in the same way or at the same pace, and it strives to provide a more engaging and effective learning journey for each one. It's a shift away from a one-size-fits-all model towards a more dynamic and responsive educational environment.
This individualized approach can significantly enhance student motivation and engagement. When students feel that their learning is relevant and tailored to their needs, they are more likely to be invested in the process and achieve better outcomes. By fostering a deeper understanding of the student's cognitive and emotional needs, personalized learning can unlock potential and create a love for learning.
Key Components of Personalized Learning
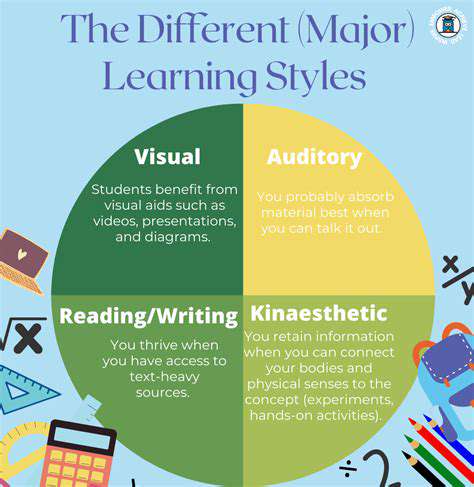
A crucial component of personalized learning is the identification of individual learning styles. This involves understanding how each student best processes information, whether it's through visual, auditory, kinesthetic, or a combination of methods. By recognizing these different approaches, educators can create learning activities that cater to diverse styles, resulting in a more enriching learning experience for all.
Further, personalized learning often incorporates adaptive learning technologies. These platforms adjust the difficulty and pace of lessons based on a student's performance, ensuring that they are consistently challenged and supported. This dynamic adjustment allows students to progress at their own speed and focus on areas where they need extra support.
Assessment plays a vital role as well. Moving beyond traditional standardized tests, personalized learning emphasizes formative assessments that provide ongoing feedback to both the student and the teacher. This iterative feedback loop allows for continuous adjustments to the learning path, ensuring the student is constantly progressing effectively.
Benefits and Challenges of Personalized Learning
The benefits of personalized learning are numerous. Students experience greater engagement and motivation as their learning becomes more relevant and tailored to their individual needs. This approach can lead to a deeper understanding of subjects, improved academic performance, and a more positive learning experience overall. This personalized approach recognizes and values each student's unique strengths and learning preferences, leading to enhanced self-efficacy and confidence.
However, implementing personalized learning also presents challenges. It requires significant resources, including time, technology, and skilled educators capable of adapting their teaching methods. The need for differentiated instruction and individualized support means a shift in the traditional classroom structure. Developing and maintaining the necessary resources and support systems can be a complex process, requiring careful planning and collaboration.
Adapting Assessment to Individual Learning Journeys

Understanding Diverse Learning Needs
Assessing students effectively requires a deep understanding of the various learning styles, paces, and challenges that individual students face. Recognizing these diverse needs is crucial for creating equitable and impactful learning experiences. Students may possess different strengths and weaknesses, and their backgrounds and experiences can profoundly influence their learning trajectories.
Consideration of factors such as cultural background, socioeconomic status, and physical or cognitive disabilities is essential. Adapting assessment strategies can help ensure that all students have the opportunity to demonstrate their knowledge and skills, regardless of their learning style or challenges.
Differentiated Assessment Strategies
Differentiated assessment strategies are vital for catering to the varying needs of learners. These strategies involve adjusting the content, process, or product of assessment to better suit individual learning styles and abilities. For instance, providing alternative formats for tasks like oral presentations, visual aids, or written responses, can significantly impact a student's ability to demonstrate their understanding.
This approach ensures that all students are assessed fairly and equitably, and that their unique strengths are highlighted. It's a critical step towards personalized learning and individualized support.
Alternative Assessment Methods
Exploring alternative assessment methods, such as portfolios, projects, and observations, can offer a more comprehensive view of a student's abilities beyond traditional testing. These methods can provide valuable insights into a student's progress and learning process, enabling teachers to identify areas where support or intervention may be needed.
Adjusting Assessment Timelines
Flexibility in assessment timelines can be a key component of accommodating individual needs. Allowing extra time for students who require it can significantly impact their performance, allowing them to demonstrate their knowledge and skills without the pressure of time constraints. This accommodation can be particularly beneficial for students with learning differences.
Using Multiple Intelligences
Recognizing and incorporating multiple intelligences into assessment can provide a more holistic understanding of student abilities. Rather than relying solely on linguistic or logical-mathematical assessments, teachers can utilize methods that tap into visual-spatial, musical, bodily-kinesthetic, interpersonal, intrapersonal, and naturalistic intelligences. This approach acknowledges the diverse ways in which students learn and process information.
Creating Inclusive Assessment Environments
An inclusive assessment environment is essential for fostering a sense of belonging and encouraging participation from all students. Creating a safe and supportive learning environment where students feel comfortable taking risks and demonstrating their knowledge is crucial to effective assessment. This environment should prioritize respect and understanding for different learning styles and needs.
Regular Communication and Feedback
Regular communication with students and their families is vital for ensuring that assessment practices are understood and that adjustments are made as needed. Providing timely and constructive feedback is crucial for supporting student learning and growth. This feedback should be tailored to individual needs and focus on specific areas for improvement.
Open communication channels, both within the classroom and with parents/guardians, create a collaborative environment where students feel supported and empowered in their learning journey.
Connecting Assessment to Learning Goals and Outcomes
Defining Learning Goals and Outcomes
Clearly defining learning goals and outcomes is crucial for effective assessment. These goals should articulate what students are expected to know, understand, and be able to do by the end of a course or program. Precisely defining learning outcomes ensures that assessment tools accurately measure student progress towards these specific objectives. Vague or overly broad goals can lead to ambiguous assessments and inaccurate evaluations of student learning.
This process involves identifying the desired knowledge, skills, and abilities students should acquire. For example, instead of a general goal like understanding history, a more specific outcome might be Students will be able to analyze primary source documents to identify historical trends. This level of specificity is essential for designing targeted and effective assessments.
Developing Aligned Assessment Strategies
Once learning goals and outcomes are established, the next step is to develop assessment strategies that directly measure student progress toward those goals. These strategies should be tailored to the specific learning outcomes, ensuring that the assessment methods accurately reflect the knowledge, skills, and abilities being evaluated. For example, if a learning outcome focuses on critical thinking, the assessment should include tasks that require students to analyze information, evaluate arguments, and formulate reasoned judgments.
Different types of assessments, such as quizzes, exams, projects, presentations, and portfolios, can be employed to measure various aspects of learning. The choice of assessment method should be carefully considered to ensure it effectively gauges student mastery of the specific learning outcomes.
Implementing and Using Assessment Data
Implementing assessment strategies effectively requires careful planning and execution. This includes providing clear instructions to students regarding the assessment tasks, ensuring that the assessment environment is conducive to fair and accurate evaluation, and promptly providing students with feedback on their performance.
Analyzing the collected assessment data is essential for understanding student learning and making necessary adjustments to teaching and learning strategies. This data provides valuable insights into student strengths and weaknesses, areas where additional support might be needed, and the overall effectiveness of the instructional materials and methods employed.
Interpreting Assessment Results
Interpreting assessment results requires a careful and thoughtful approach. Educators should avoid jumping to conclusions based on superficial observations. Instead, a comprehensive analysis of the data is needed to identify patterns and trends in student performance. This includes considering individual student progress, class performance as a whole, and the alignment between assessment results and the established learning goals and outcomes.
Qualitative data, such as student feedback and observations during presentations, should also be considered when interpreting assessment data. A holistic understanding of student learning is crucial for making informed decisions about instruction and support.
Linking Assessment to Continuous Improvement
The process of connecting assessment to learning goals and outcomes is not a one-time event; it's a cyclical process that supports continuous improvement. Regularly reviewing assessment data and reflecting on the effectiveness of instruction are essential steps in this process. Using this feedback, educators can refine their teaching strategies, adjust course materials, and provide targeted support to students who may be struggling.
By actively incorporating assessment data into the instructional cycle, educators can create a more dynamic and responsive learning environment that fosters student success and ensures that learning outcomes are consistently met.
Read more about Measuring Cognitive Outcomes in Personalized Learning Environments
Hot Recommendations
- The Gamified Parent Teacher Conference: Engaging Stakeholders
- Gamification in Education: Making Learning Irresistibly Fun
- The Future of School Libraries: AI for Personalized Recommendations
- EdTech and the Future of Creative Industries
- Empowering Student Choice: The Core of Personalized Learning
- Building Community in a Hybrid Learning Setting
- VR for Special Education: Tailored Immersive Experiences
- Measuring the True Value of EdTech: Beyond Adoption Rates
- Addressing Digital Divide in AI Educational Access
- Preparing the Workforce for AI Integration in Their Careers