Hybrid Learning for Higher Education: Best Practices and Tools
Defining Hybrid Learning in Higher Education

Defining Hybrid Learning in Higher Education
Hybrid learning, often referred to as blended learning, embodies an educational strategy that thoughtfully merges digital and face-to-face instructional methods. This adaptable teaching framework capitalizes on the unique advantages of each delivery mode to cultivate a more dynamic and participatory academic atmosphere. By weaving together instructor-led sessions with self-paced digital components, learners can enjoy a customized educational pathway tailored to individual needs.
Central to this approach is the purposeful incorporation of digital materials and tasks that complement conventional classroom teaching. These might encompass interactive learning units, recorded lectures, online discussion boards, and group assignments - all crafted to enrich comprehension while permitting students to progress according to their personal learning rhythms.
Key Characteristics of Hybrid Learning
Successful hybrid programs demonstrate meticulous curriculum architecture. The equilibrium between digital and physical components requires deliberate planning to ensure both contribute substantially toward educational goals. This intentional design should incorporate both real-time and self-paced learning opportunities, accommodating diverse schedules and learning preferences.
Educators play a pivotal role in this model, transitioning between digital and physical spaces to mentor students effectively. Their responsibilities extend to nurturing an inclusive and stimulating academic environment across both platforms, encouraging peer interaction and collective knowledge building.
Benefits of Hybrid Learning for Students
This educational model provides significant advantages regarding scheduling flexibility and universal access. Learners can review materials and complete assignments when convenient, particularly valuable for those balancing multiple responsibilities or residing in distant locations.
Additionally, this approach stimulates more participatory and cooperative educational experiences. Digital platforms facilitate ongoing academic dialogue beyond traditional classroom boundaries, strengthening peer connections and collaborative learning opportunities.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing Hybrid Learning
While offering numerous benefits, this model presents implementation hurdles. Reliable technological infrastructure represents a fundamental requirement, ensuring all participants can access necessary digital tools and stable internet connections.
Establishing comprehensive support systems proves equally critical. Transparent communication pathways and readily available assistance mechanisms must exist to address student inquiries promptly across both learning environments, necessitating well-developed digital platforms and dedicated support personnel.
Crafting Effective Hybrid Course Design
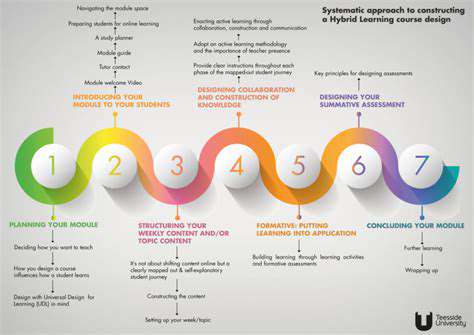
Designing Engaging Learning Experiences
Developing compelling academic activities that resonate with both physical and remote participants forms the cornerstone of successful hybrid programs. This demands careful selection of instructional materials, interactive components, and evaluation methods that optimize student involvement and knowledge retention. Incorporating digital collaboration tools, virtual simulations, and online debates can substantially enrich the educational journey for distance learners.
Bridging the gap between classroom and online participants remains essential for creating cohesive learning communities. Strategic planning of joint activities like digital study groups, collaborative assignments, or shared virtual experiences fosters meaningful connections across learning modalities.
Balancing Synchronous and Asynchronous Activities
Effective hybrid curricula maintain equilibrium between scheduled interactive sessions and flexible learning components. Live instructional periods enable immediate clarification of concepts and vibrant academic discourse, while self-paced materials accommodate varying schedules and learning velocities.
Utilizing Technology Effectively
Selection of appropriate digital tools significantly impacts program success. The chosen learning management system should integrate effortlessly with collaboration software and multimedia resources while remaining intuitive for all users. Comprehensive orientation materials and responsive technical support prove indispensable for maintaining smooth program operation.
Assessment Strategies for Hybrid Learning
Evaluation methods should reflect the blended nature of instruction, incorporating diverse formats to accommodate different learning preferences. A mixture of written submissions, oral presentations, and group projects provides multiple avenues for demonstrating comprehension while assessing both individual and collaborative skills.
Course Structure and Communication
Transparent organizational frameworks and consistent information sharing establish the foundation for successful hybrid programs. Detailed syllabi outlining expectations, timelines, and evaluation criteria combined with regular updates and accessible instructor availability create structured yet flexible learning environments. Establishing predictable communication rhythms through multiple channels ensures all participants remain informed and engaged throughout the academic term.
Facilitating Effective Communication and Collaboration
Enhancing Communication Channels
Robust digital infrastructure forms the backbone of successful hybrid programs, enabling seamless interaction among all participants. Multiple communication pathways including discussion boards, video platforms, and messaging systems should be implemented with clear usage guidelines to maintain productive academic discourse.
Streamlining Collaboration Tools
Digital collaboration platforms enable collective knowledge construction and resource sharing. When properly integrated with course management systems and accompanied by comprehensive training materials, these tools can significantly enhance group learning experiences.
Fostering a Sense of Community
Intentional community-building activities help overcome the physical separation inherent in hybrid models. Scheduled virtual gatherings, academic showcases, and informal digital meetups can cultivate meaningful connections among participants.
Adapting Communication Strategies
Effective hybrid instruction requires flexible communication approaches that accommodate diverse learning preferences. Combining scheduled interactive sessions with ongoing asynchronous discussions ensures all participants can engage according to their individual circumstances and preferences.
Addressing Potential Challenges
Proactive measures can mitigate common hybrid learning obstacles. Comprehensive technical support, flexible scheduling options, and digital literacy resources help overcome technological barriers, while establishing norms for respectful interaction promotes inclusive learning environments.
Read more about Hybrid Learning for Higher Education: Best Practices and Tools
Hot Recommendations
- The Gamified Parent Teacher Conference: Engaging Stakeholders
- Gamification in Education: Making Learning Irresistibly Fun
- The Future of School Libraries: AI for Personalized Recommendations
- EdTech and the Future of Creative Industries
- Empowering Student Choice: The Core of Personalized Learning
- Building Community in a Hybrid Learning Setting
- VR for Special Education: Tailored Immersive Experiences
- Measuring the True Value of EdTech: Beyond Adoption Rates
- Addressing Digital Divide in AI Educational Access
- Preparing the Workforce for AI Integration in Their Careers