Gamified Teacher Professional Development: Skill Building Through Play
Measuring the Impact of Gamification

Understanding Gamification in a Business Context
Gamification, the application of game design elements to non-game contexts, is increasingly used in business settings to enhance engagement and motivation. This approach can significantly improve employee productivity and customer loyalty by fostering a sense of achievement and accomplishment. It's not simply about adding points and leaderboards, but about incorporating game mechanics to drive desired behaviors and outcomes.
Companies are leveraging gamification to improve various aspects of their operations, such as employee training, customer service interactions, and even internal communication. By making tasks more engaging and rewarding, gamification can transform mundane activities into stimulating experiences.
Key Gamification Elements and Their Impact
Several key elements are crucial to successful gamification. These include points, badges, leaderboards, and challenges. Points and badges provide tangible recognition for achievements, fostering a sense of accomplishment and encouraging continued participation. Leaderboards, while potentially controversial, can drive healthy competition and motivation. Challenges, designed to be progressively more difficult, encourage skill development and mastery.
Implementing these elements effectively requires a deep understanding of the target audience and the desired behaviors. A poorly designed gamification strategy can backfire, leading to frustration and demotivation rather than the intended positive outcomes.
Measuring the Effectiveness of Gamification Initiatives
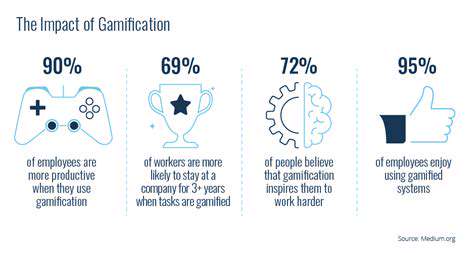
Measuring the impact of gamification is paramount to understanding its effectiveness and optimizing future implementations. Key metrics to track include participation rates, completion rates of tasks, and improvements in performance metrics directly related to the gamified activities. Monitoring these metrics allows companies to identify what's working and what needs adjustment to maximize the benefits.
Considerations for Different Business Applications
The application of gamification principles varies across different business functions. For instance, in sales, gamification can be used to encourage higher sales quotas through leaderboards and reward systems. In customer service, gamification can incentivize positive interactions and feedback collection. Considering the specific objectives and context of each application is critical to design effective and impactful gamification strategies.
Challenges and Ethical Implications of Gamification
While gamification offers significant potential, it's not without its challenges. One such challenge is the potential for negative social dynamics, such as unhealthy competition or pressure to perform. Another is the need for careful consideration of ethical implications, especially when dealing with sensitive data or vulnerable populations. Careful planning and ethical considerations are essential to ensure that gamification strategies benefit all stakeholders and avoid unintended consequences. Implementing clear guidelines and limitations are essential for a successful and ethical approach.
The Future of Teacher Training: Embracing Play-Based Learning
Innovative Approaches to Play-Based Learning
Play-based learning is rapidly gaining traction as a powerful pedagogical tool, offering a refreshing alternative to traditional rote memorization. It fosters creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills in a fun and engaging environment. Integrating play into teacher training programs will equip educators with the knowledge and practical skills to effectively design and implement play-based learning activities, making learning more interactive and enjoyable for students of all ages and learning styles. This shift moves beyond passive instruction to active participation and exploration.
A key element of this innovative approach involves understanding how play fosters cognitive development. By incorporating games, simulations, and imaginative scenarios, educators can create a learning environment where students actively construct knowledge through exploration and experimentation. This approach not only enhances understanding but also encourages collaboration, communication, and social-emotional development. This is a critical aspect of modern education, nurturing well-rounded individuals ready to tackle the challenges of the 21st century.
Gamifying Teacher Development
Integrating game mechanics into teacher training programs can significantly enhance engagement and knowledge retention. Think of interactive simulations where aspiring teachers can practice classroom management strategies in a safe and supportive environment. Gamified modules can track progress, provide personalized feedback, and offer opportunities for collaboration among participants. This approach not only makes the training experience more engaging but also helps teachers develop critical skills in a dynamic and motivating context.
Gamification can also be used to reinforce key pedagogical concepts. For example, a teacher training program could incorporate a game where participants are challenged to design and implement different lesson plans. This interactive approach allows teachers to experiment with various teaching styles, receive immediate feedback, and refine their strategies in a supportive environment. This can lead to a more confident and effective teaching practice, ultimately benefiting the students they serve.
Adapting to Diverse Learning Needs
Play-based learning provides a flexible framework that can be adapted to meet the diverse learning needs of students. By incorporating various types of play, teachers can cater to different learning styles, abilities, and interests. For instance, some students might thrive in collaborative games, while others might excel in individual challenges. A well-designed play-based learning environment respects and accommodates these differences, ensuring that every student has the opportunity to learn and grow at their own pace.
Furthermore, play-based learning can be highly effective in addressing specific learning challenges. For example, students with special needs can benefit from adapted games and activities that promote their specific learning goals. This inclusive approach ensures that all students feel valued, supported, and empowered to participate fully in the learning process. By creating a supportive and engaging environment, educators can unlock the potential of every learner.
Read more about Gamified Teacher Professional Development: Skill Building Through Play
Hot Recommendations
- The Gamified Parent Teacher Conference: Engaging Stakeholders
- Gamification in Education: Making Learning Irresistibly Fun
- The Future of School Libraries: AI for Personalized Recommendations
- EdTech and the Future of Creative Industries
- Empowering Student Choice: The Core of Personalized Learning
- Building Community in a Hybrid Learning Setting
- VR for Special Education: Tailored Immersive Experiences
- Measuring the True Value of EdTech: Beyond Adoption Rates
- Addressing Digital Divide in AI Educational Access
- Preparing the Workforce for AI Integration in Their Careers