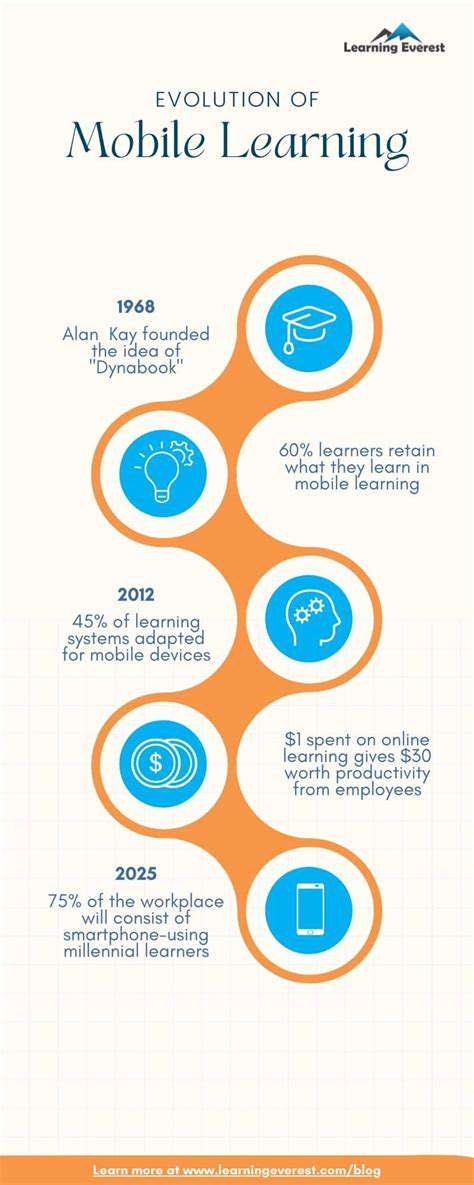
AI for Differentiated Instruction: Tailoring Education to Every Learner
Understanding the Foundations of Perception
Human perception has shaped our cognitive framework since antiquity, serving as the lens through which we interpret our surroundings. This intricate system transforms raw sensory data into coherent experiences, enabling effective interaction with our environment. Far from being passive, perception actively constructs reality through the interplay of prior knowledge and anticipatory frameworks. This adaptive mechanism allows pattern recognition, object identification, and decision-making despite incomplete data. For centuries, scholars have grappled with whether perception mirrors objective truth or remains fundamentally subjective - a debate that continues to inform contemporary psychological and neurological research.
Historical Perspectives and Key Theories
The intellectual journey of perceptual studies reveals fascinating evolutionary patterns. Ancient Greek philosophers established foundational concepts that later thinkers would expand upon, with Plato emphasizing innate structures while Aristotle championed empirical observation. The scientific revolution birthed experimental psychology, yielding Gestalt theory's influential perspective on holistic perception. Modern neuroscience has since mapped the neural pathways that convert sensory signals into conscious experience. These cumulative discoveries highlight perception's pivotal role in shaping human cognition and behavioral responses across diverse contexts.
Modern Developments and Future Directions
Contemporary perceptual research represents a convergence of multiple disciplines, blending psychological insights with cutting-edge technology. Advanced imaging techniques and virtual environments now permit real-time observation of perceptual processes under controlled conditions. The emergence of machine learning has particularly revolutionized our capacity to simulate human perception, offering unprecedented modeling capabilities. Future investigations promise to decode the neural mysteries behind phenomena like sensory integration and conscious awareness, potentially unlocking new dimensions in our comprehension of mental processes and subjective reality.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations in AI-Enhanced Differentiated Instruction
Data Bias and Equity
One pressing issue involves the potential reinforcement of societal biases through AI training datasets. When historical data reflects systemic inequalities, algorithmic outputs may inadvertently perpetuate these patterns in educational recommendations. This risk demands rigorous dataset curation and continuous bias monitoring to prevent exacerbating achievement disparities among student populations.
Transparency and Explainability
The opacity of certain AI decision-making processes creates significant implementation barriers. Without clear understanding of how algorithms generate instructional suggestions, educators may struggle to validate or appropriately apply these recommendations. Developing interpretable AI systems remains crucial for building trust and ensuring responsible classroom integration.
Teacher Agency and Collaboration
Effective implementation requires positioning AI as a supportive tool rather than an autonomous authority. Professional development programs must empower educators to critically evaluate and adapt AI-generated insights within their established pedagogical frameworks. Creating communities of practice allows teachers to share implementation strategies and collectively refine their technology integration approaches.
Assessment and Evaluation
Traditional metrics often fail to capture the multidimensional outcomes of AI-enhanced instruction. Developing specialized assessment frameworks that measure both academic progress and affective factors like engagement represents a critical need. These evaluation tools must themselves undergo rigorous bias testing to ensure equitable application across diverse learner populations.
Privacy and Data Security
The collection and analysis of student data introduces substantial confidentiality concerns. Compliance with privacy regulations constitutes only the baseline requirement - institutions must implement robust cybersecurity measures and transparent data governance policies. Clear communication with stakeholders about data usage protocols helps maintain trust while protecting sensitive information.
Accessibility and Inclusivity
AI educational tools must undergo universal design testing to ensure accessibility for learners with diverse needs. This includes accommodating physical disabilities, language differences, and varied learning preferences through adaptable interfaces and multimodal content delivery. Continuous user feedback loops enable iterative improvements that expand equitable access to AI-enhanced learning benefits.
Read more about AI for Differentiated Instruction: Tailoring Education to Every Learner
Hot Recommendations
- The Gamified Parent Teacher Conference: Engaging Stakeholders
- Gamification in Education: Making Learning Irresistibly Fun
- The Future of School Libraries: AI for Personalized Recommendations
- EdTech and the Future of Creative Industries
- Empowering Student Choice: The Core of Personalized Learning
- Building Community in a Hybrid Learning Setting
- VR for Special Education: Tailored Immersive Experiences
- Measuring the True Value of EdTech: Beyond Adoption Rates
- Addressing Digital Divide in AI Educational Access
- Preparing the Workforce for AI Integration in Their Careers