EdTech for Social Impact: Education as a Force for Good
Cultivating Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving Skills in the Digital Age
Cultivating a Growth Mindset
Developing critical thinking skills is inextricably linked to fostering a growth mindset. A growth mindset embraces challenges and views setbacks as opportunities for learning and improvement. This proactive approach is crucial for analyzing information objectively and forming reasoned judgments. Individuals with a growth mindset are more likely to engage in self-reflection and actively seek out diverse perspectives, essential components of critical thinking. This mindset encourages continuous learning, a vital attribute for navigating the complexities of the modern world.
Cultivating a growth mindset involves recognizing that intelligence and abilities are not fixed traits. Instead, they are developed through dedication, hard work, and a willingness to embrace challenges. This understanding empowers individuals to approach learning and problem-solving with a persistent attitude, rather than feeling limited by perceived limitations.
Identifying and Evaluating Sources
A cornerstone of critical thinking is the ability to discern credible sources from unreliable ones. Evaluating sources involves scrutinizing their author's expertise, the methodology used to gather and analyze information, and the potential biases that might influence the presented data. Recognizing potential biases is critical to forming objective judgments.
Thorough research and source evaluation are paramount in forming accurate conclusions. This process ensures that the information used to support arguments is dependable and relevant. Poorly researched arguments often lack the necessary foundation and credibility.
Analyzing Arguments and Identifying Biases
Critical thinkers are adept at dissecting arguments, identifying underlying assumptions, and recognizing potential biases. This involves scrutinizing the logical structure of the argument, identifying any fallacies or weaknesses in reasoning, and understanding the potential motivations of the arguer. Recognizing biases in arguments is essential for forming well-reasoned opinions.
Applying Logic and Reasoning Skills
Critical thinking requires the application of logical reasoning skills to analyze information and draw conclusions. This involves identifying patterns, making connections, and evaluating the validity of inferences. Strong logical reasoning skills enable individuals to distinguish between sound and unsound arguments and to form well-supported conclusions.
Furthermore, critical thinkers understand the importance of considering multiple perspectives and acknowledging the limitations of their own understanding. This awareness of limitations is crucial for fostering intellectual humility. A crucial aspect of critical thinking is the ability to adapt and refine one's understanding in response to new information and evidence. This adaptability is essential for navigating the complexities of a constantly evolving world.
Empowering Educators with Innovative Tools and Resources

Innovative Pedagogical Approaches
Empowering educators with innovative pedagogical approaches is crucial for fostering a dynamic and engaging learning environment. These approaches go beyond traditional methods, incorporating diverse strategies that cater to the unique learning styles and needs of students. This shift demands a willingness to embrace new technologies and methodologies, fostering creativity and critical thinking skills in students. This necessitates a continuous cycle of professional development and collaboration among educators to ensure effective implementation.
By exploring innovative pedagogical approaches, educators can cultivate a love for learning in their students, making the classroom a vibrant hub of intellectual curiosity. This exploration should consider various learning modalities, from visual and auditory to kinesthetic and tactile, ensuring inclusivity and understanding for all learners.
Leveraging Technology in Education
Integrating technology effectively into the educational landscape is paramount for empowering educators. The digital age presents incredible opportunities to enhance teaching and learning experiences. Tools such as interactive whiteboards, online learning platforms, and educational software can transform the classroom from a passive lecture hall to an active, collaborative learning space.
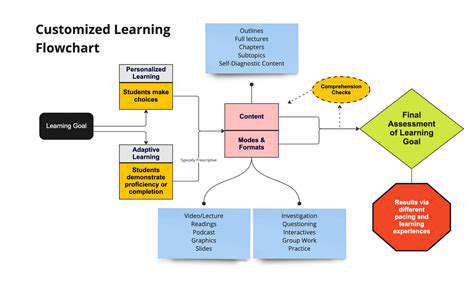
Modern technology allows for personalized learning paths, enabling educators to tailor instruction to individual student needs. This personalized approach can significantly improve student engagement and academic outcomes, fostering a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Cultivating Collaborative Learning Environments
Collaborative learning environments are essential for empowering educators. These environments foster a sense of community and shared responsibility among students. By encouraging teamwork and peer-to-peer learning, educators can nurture crucial social-emotional skills, such as communication, empathy, and conflict resolution.
Such an approach not only enhances academic performance but also promotes a more positive and supportive classroom culture. These environments empower students to learn from one another, fostering a deeper understanding of diverse perspectives and promoting intellectual growth.
Promoting Student-Centered Learning
Student-centered learning places the student at the heart of the educational process, recognizing their individual needs and aspirations. This approach requires educators to adapt their teaching methods to cater to diverse learning styles and preferences. By actively engaging students in the learning process, educators can cultivate a deeper understanding and more enduring knowledge.
A student-centered learning environment empowers students to take ownership of their learning, fostering intrinsic motivation and a love of lifelong learning. This approach emphasizes active participation, inquiry-based learning, and the development of critical thinking skills.
Enhancing Teacher Professional Development
Continuous professional development is a cornerstone of empowering educators. It equips teachers with the necessary knowledge, skills, and tools to implement innovative pedagogical approaches effectively. This ongoing development can encompass workshops, seminars, online courses, and mentorship programs, designed to enhance teaching practices and address the evolving needs of students.
Investing in teacher professional development is an investment in the future of education. By providing educators with opportunities to learn and grow, we are empowering them to create dynamic, engaging, and impactful learning experiences for all students.
Measuring and Evaluating the Impact of EdTech Initiatives
Defining Measurable Impact
A crucial first step in evaluating EdTech initiatives is clearly defining what constitutes impact. Simply measuring engagement metrics like time spent on a platform or completion rates isn't enough to demonstrate true social impact. We need to delve deeper, considering the specific learning outcomes, skill development, and behavioral changes that the EdTech is intended to foster. This requires a thoughtful analysis of the target population and the specific educational goals, ensuring that the metrics align with the desired outcomes and are relevant to the context of the initiative.
Defining measurable impact also necessitates setting realistic expectations. EdTech is not a silver bullet. The impact of an EdTech initiative is rarely immediate and is often intertwined with other factors, such as pre-existing educational infrastructure, teacher training, and student motivation. Recognizing these complexities is essential for developing appropriate evaluation strategies.
Assessing Learning Outcomes
One of the most critical aspects of evaluating EdTech initiatives is measuring learning outcomes. This includes assessing student knowledge acquisition, skill development, and improvements in critical thinking. This can be achieved through pre- and post-tests, standardized assessments, or other relevant evaluation tools. The choice of assessment methods should be carefully considered, ensuring they align with the learning objectives and accurately capture the desired learning outcomes.
Beyond traditional assessments, qualitative data, such as student feedback and observations, can provide valuable insights into the learning experience. Gathering student perspectives on the effectiveness of the EdTech tools, their ease of use, and their perceived value can help to identify areas for improvement and tailor the EdTech to better meet the needs of the students.
Analyzing Student Engagement and Motivation
Student engagement and motivation are vital components of successful EdTech implementations. Measuring factors like active participation, collaborative learning, and intrinsic motivation can provide a deeper understanding of the effectiveness of the EdTech in fostering a positive learning environment. Tools for tracking student engagement, such as platform usage data, participation in online discussions, and feedback mechanisms, can be invaluable in this assessment process.
Considering Equity and Accessibility
A comprehensive evaluation of EdTech initiatives must consider equity and accessibility. Does the EdTech provide equal opportunities for all students, regardless of their background, socioeconomic status, or learning needs? Evaluating access to technology, internet connectivity, and training support is crucial. Furthermore, assessing whether the EdTech exacerbates existing inequalities or promotes inclusivity is essential for maximizing its potential for social impact.
Data collection methods that capture the experiences of diverse student populations are crucial. Gathering feedback from students from various backgrounds can help to identify potential biases or barriers to access and ensure that the EdTech is inclusive and equitable for all.
Evaluating the Sustainability and Scalability of the Initiative
Beyond immediate impact, the sustainability and scalability of an EdTech initiative are essential for long-term social impact. Can the initiative be implemented and maintained over time, even with changing resources and personnel? Assessing the financial viability, operational efficiency, and potential for replication across different contexts are important considerations. This includes examining the necessary infrastructure, training requirements for teachers, and the potential for community engagement.
Furthermore, evaluating the potential for scaling the initiative to reach a wider audience is crucial. Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful scaling, such as adaptable design, robust support systems, and effective training models, will help to ensure that the positive impact of the EdTech can reach a greater number of students and communities.
Read more about EdTech for Social Impact: Education as a Force for Good
Hot Recommendations
- The Gamified Parent Teacher Conference: Engaging Stakeholders
- Gamification in Education: Making Learning Irresistibly Fun
- The Future of School Libraries: AI for Personalized Recommendations
- EdTech and the Future of Creative Industries
- Empowering Student Choice: The Core of Personalized Learning
- Building Community in a Hybrid Learning Setting
- VR for Special Education: Tailored Immersive Experiences
- Measuring the True Value of EdTech: Beyond Adoption Rates
- Addressing Digital Divide in AI Educational Access
- Preparing the Workforce for AI Integration in Their Careers