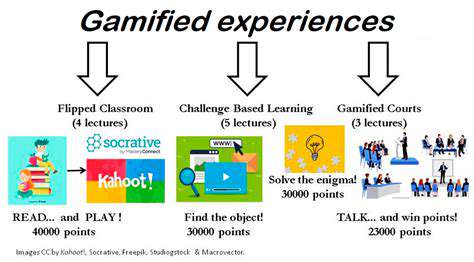
Designing Ethical Gamification: Avoiding Pitfalls and Promoting Well being
Understanding Intrinsic Motivation
At its essence, intrinsic motivation represents the impulse to pursue activities for personal fulfillment rather than external incentives. This internal drive powers learning, exploration, and innovation absent outside pressures. Grasping this fundamental human trait proves critical when creating compelling experiences, especially within gamification. When we engage this natural motivation, we establish profound connections with tasks, yielding greater perseverance and originality.
Designing for Curiosity and Exploration
Curiosity serves as a cornerstone of intrinsic motivation. Gamified environments should stimulate investigation and revelation through thoughtfully constructed obstacles, unexpected developments, and avenues for adaptation. By engineering systems that spark fascination, we access humanity's innate urge to solve puzzles and conquer barriers, rendering the activity inherently satisfying.
Allowing participants to uncover fresh tactics, hidden features, or alternative perspectives deepens involvement and autonomy. This sense of control feeds intrinsic motivation as users actively mold their journey.
Building a Sense of Mastery and Progress
The sensation of development and proficiency motivates powerfully. Gamification should delineate clear routes for skill enhancement and milestone attainment. Incremental objectives paired with instant feedback and visible advancement generate mastery feelings that sustain interaction. This structure reinforces constructive cycles, making the learning process itself rewarding.
Fostering Collaboration and Social Connection
Human interaction significantly influences intrinsic motivation. Gamified designs incorporating cooperative elements and social bonds can dramatically improve engagement. Chances for teamwork, knowledge exchange, and friendly competition nurture community and inclusion. This social dimension adds motivational layers, converting solitary endeavors into collective adventures.
Creating Meaningful Experiences and Purpose
Beyond mechanical aspects, connecting with participants' values and aspirations proves essential. Gamification aligning with personal beliefs and ambitions forges deeper bonds. Incorporating resonant themes, chances to contribute to larger causes, and personal evolution opportunities can make activities profoundly meaningful. When experiences carry significance, engagement stems from within rather than external inducements.
Chronic pain extends beyond physical suffering—it's an enduring state that transforms existence. Unlike transient discomfort that dissipates, chronic pain persists beyond three months, disturbing rest, affecting emotions, and constraining routines. Chronic pain's complexity lies in its capacity to transcend initial causes, establishing new neural connections that perpetuate distress. Effective management requires unraveling these intricate patterns through coordinated patient-provider efforts.
Transparency and User Control: Empowering the Player
Transparency in Game Design
Game design transparency proves fundamental for ethical, positive player interactions. Participants should understand mechanics, reward distribution, and any inherent system biases or constraints. Explicitly detailing regulations, aims, and action consequences builds confidence and enables informed engagement decisions.
Open dialogue regarding development processes, including prospective modifications, further enhances clarity. This proactive communication resolves concerns quickly and preserves trust amid unexpected changes.
User Control over Progression
Granting participants progression autonomy remains crucial for ethical gamification. This might involve choosing individual paths, customizing avatars, or setting personal targets. Such independence fosters ownership and commitment, yielding richer, more personalized experiences.
Minimizing undue achievement pressures proves necessary. Excessive demands may cause frustration or self-doubt. Permitting adjustable pacing and approaches encourages healthy, sustainable involvement.
Accountability and Fair Play
Gamification should champion equitable participation and responsibility. This entails defining prohibited behaviors precisely and instituting prevention and resolution measures. A clear reporting process and consistent enforcement maintain fair, respectful gaming ecosystems.
Establishing explicit behavioral standards helps prevent disputes and ensures all feel appreciated. Recognizing diverse play styles and avoiding preferential treatment for specific approaches remains vital, including unambiguous rule presentation.
Managing Gamification's Impact on Motivation
While gamification motivates powerfully, addressing potential drawbacks matters. Systems should avoid extreme competition, pressure, or coercion. Prioritizing internal motivation over external rewards creates more enduring, satisfying experiences, preventing reward fixation at the expense of genuine enjoyment.
Addressing Potential Biases and Inequalities
Gamification must circumvent bias reinforcement or inequality creation. Considerations should include cultural variations, accessibility requirements, and resource disparities. Designs must account for differing resource access and experience levels.
Regular evaluations across participant demographics help identify and rectify inadvertent biases. Soliciting diverse feedback and making continuous refinements ensures inclusive, equitable engagement for all.
Balancing Fun and Meaning
Effective gamification merges entertainment with significance. Games can incorporate thought-provoking themes that inspire learning and self-improvement. Facilitating connections and relationship-building through play enriches overall experiences.
Optimal systems strike equilibrium between enjoyment and substance, avoiding excessive focus on superficial aspects. Integrating narratives, challenges, and growth opportunities achieves this balance.
Read more about Designing Ethical Gamification: Avoiding Pitfalls and Promoting Well being
Hot Recommendations
- The Gamified Parent Teacher Conference: Engaging Stakeholders
- Gamification in Education: Making Learning Irresistibly Fun
- The Future of School Libraries: AI for Personalized Recommendations
- EdTech and the Future of Creative Industries
- Empowering Student Choice: The Core of Personalized Learning
- Building Community in a Hybrid Learning Setting
- VR for Special Education: Tailored Immersive Experiences
- Measuring the True Value of EdTech: Beyond Adoption Rates
- Addressing Digital Divide in AI Educational Access
- Preparing the Workforce for AI Integration in Their Careers