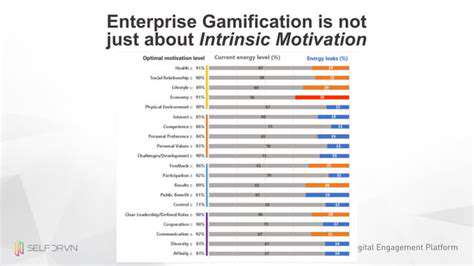
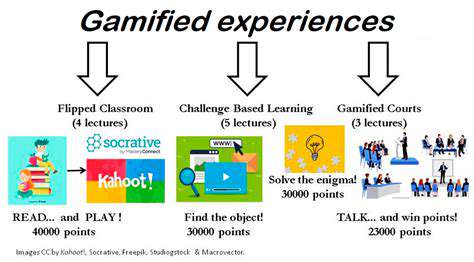
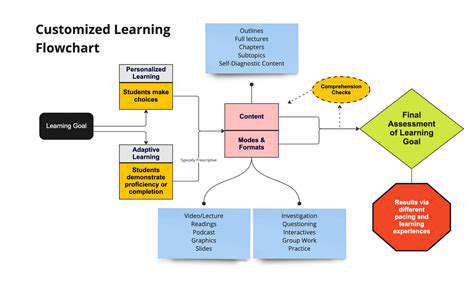
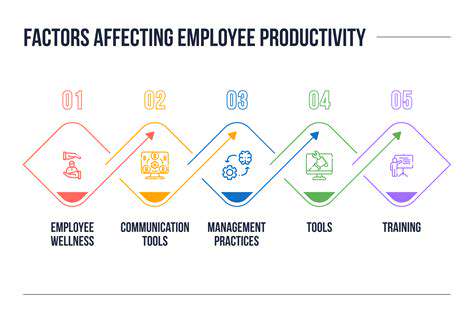
Personalized AI Learning: Tailoring Education to Individual Needs
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming healthcare, offering innovative solutions for diagnostics. AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets of medical images, patient records, and genetic information to identify patterns and anomalies that might be missed by human clinicians. This technology holds immense promise for early disease detection and personalized treatment plans. AI-powered diagnostics can potentially improve accuracy and efficiency in healthcare delivery, benefiting both patients and healthcare providers.
The ability of AI to process massive amounts of data allows for the identification of subtle indicators of disease that might be overlooked by the human eye. This can lead to earlier intervention and improved patient outcomes.
Adaptive Learning in AI Systems
AI systems are not static; they constantly learn and adapt to new information. This adaptive learning capability is crucial for maintaining accuracy and reliability in diagnoses. As more data becomes available, AI algorithms refine their models, improving their ability to identify patterns and predict outcomes. This iterative learning process is essential for ensuring AI systems remain relevant and effective in the dynamic field of medicine.
Enhanced Accuracy and Efficiency
AI-powered diagnostic tools can significantly enhance the accuracy and efficiency of medical diagnoses. By analyzing complex data sets, these tools can provide more precise and reliable results compared to traditional methods. Furthermore, AI's ability to automate tasks can streamline workflows, reducing diagnostic time and improving overall efficiency in healthcare facilities.
These improvements in accuracy and speed are critical for timely interventions, which can greatly impact patient health outcomes. Faster diagnoses allow for faster treatments, reducing the time it takes to get patients the care they need.
Personalized Treatment Plans
AI can also play a pivotal role in developing personalized treatment plans for patients. By analyzing individual patient data, including medical history, genetic makeup, and lifestyle factors, AI algorithms can identify the most effective treatment strategies for each patient. This personalized approach can lead to improved treatment outcomes and reduced side effects.
Improved Patient Outcomes
The integration of AI-powered diagnostics and adaptive learning systems into healthcare practices is expected to significantly improve patient outcomes. Earlier and more accurate diagnoses enable faster interventions, reducing the severity of conditions and improving the quality of life for patients. The potential for preventing disease through early detection is a major benefit, potentially saving lives.
Ethical Considerations and Challenges
While AI offers immense potential for revolutionizing healthcare diagnostics, it's crucial to address the ethical considerations and challenges associated with its implementation. Issues such as data privacy, algorithmic bias, and the need for human oversight need careful consideration. Furthermore, ensuring the accessibility and affordability of AI-powered diagnostic tools for all patients is paramount.
Future Applications and Research
The future of AI in diagnostics looks promising, with ongoing research focusing on expanding the scope of applications. Researchers are exploring the use of AI in various medical fields, including radiology, pathology, and cardiology. Further advancements in AI technology and data availability will likely lead to even more sophisticated and reliable diagnostic tools in the years to come. The long-term goal is to develop AI systems that can improve diagnostics and care for everyone, regardless of socioeconomic status.
Modern digital systems face growing vulnerabilities as cybercriminals develop increasingly sophisticated attack methods. The exposure of personal data through security lapses can trigger cascading consequences, from financial fraud to psychological trauma. Beyond individual victims, organizational credibility often suffers lasting damage when customer trust erodes following high-profile incidents. Implementing comprehensive protective measures while understanding system weaknesses forms the foundation of effective risk management.
Ethical Considerations and Future Trends

Ethical Implications of AI Development
The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) presents a myriad of ethical dilemmas that demand careful consideration. From algorithmic bias in facial recognition software to the potential for autonomous weapons systems, the ethical implications of AI are profound and far-reaching. These concerns extend beyond simply ensuring that AI systems function correctly; they require a proactive approach to addressing the potential harms and ensuring responsible development and deployment.
One crucial aspect is the issue of algorithmic bias. AI systems are trained on vast datasets, and if these datasets reflect existing societal biases, the AI will inevitably perpetuate and even amplify them. This can lead to discriminatory outcomes in areas like loan applications, hiring processes, and even criminal justice. Careful attention must be paid to data collection practices and algorithm design to mitigate these risks and promote fairness and equity.
Ensuring Transparency and Accountability
Transparency in AI decision-making processes is paramount. Users deserve to understand how AI systems arrive at their conclusions, particularly in critical domains such as healthcare and finance. This transparency is essential for building trust and ensuring accountability, allowing for scrutiny and correction of potential errors or biases.
Accountability mechanisms are also crucial. Who is responsible when an AI system makes a harmful decision? Establishing clear lines of responsibility and implementing robust oversight mechanisms are essential to prevent unintended consequences and to ensure that AI systems are used ethically and responsibly.
The Future of AI and Human Society
The integration of AI into various aspects of human life is accelerating, prompting a critical reflection on the future of work, education, and social structures. The potential displacement of human labor by AI raises concerns about economic inequality and the need for retraining and upskilling initiatives.
Furthermore, the increasing reliance on AI systems necessitates a careful consideration of the potential impact on human autonomy and dignity. As AI systems become more sophisticated, questions about their role in decision-making, particularly in areas that affect fundamental rights, must be addressed thoughtfully and proactively. Moreover, the long-term societal impact of widespread AI adoption remains uncertain, and ongoing research and public dialogue are needed to navigate this complex landscape.
The future of AI is intertwined with the future of humanity. We must approach this technological revolution with a balanced perspective, prioritizing ethical considerations and societal well-being alongside innovation and progress.