Data Privacy Regulations in EdTech: GDPR and Beyond
Beyond the Basics: Understanding Regional Data Privacy Regulations
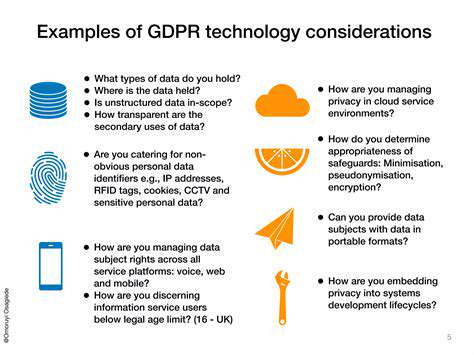
While the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) represents a significant milestone in data privacy legislation, its jurisdiction remains confined to the European Union. Across the globe, various nations and regions are actively crafting their own distinct data protection frameworks. This creates a dynamic and often confusing environment for multinational corporations. These evolving policies don't merely represent legal requirements; they embody fundamental societal attitudes toward personal information protection.
Companies must adopt forward-thinking strategies regarding data management, carefully evaluating their practices in every operational territory. Neglecting these developing standards could result in substantial financial penalties and harm to brand reputation, especially within today's interconnected business world. Such vigilance proves essential for maintaining consumer confidence and preventing potential compliance violations.
Key Differences and Considerations
Regional regulations frequently diverge from GDPR's focus on individual rights and disclosure requirements. Certain jurisdictions might emphasize specialized industries such as medical services or banking, while others prioritize strict limitations on data collection. Recognizing these variations becomes critical for preventing regulatory missteps and ensuring full adherence.
Enforcement methods also show considerable variation. Unlike GDPR's well-established oversight system, some regional authorities may possess more limited monitoring capabilities. Consequently, the severity of consequences for violations can fluctuate dramatically depending on location.
Navigating the Complexities of Global Compliance
Multinational enterprises require tailored approaches to satisfy diverse jurisdictional demands. This involves creating specific data management guidelines, deploying suitable protective technologies, and educating staff about regional legal expectations. Standardized solutions rarely prove effective - each market demands individual analysis.
Additionally, businesses must remain alert to legislative updates across all operational territories. The regulatory environment continues evolving rapidly, necessitating constant attention. Frequent policy reviews and compliance evaluations help mitigate risks and demonstrate commitment to data protection. This ongoing diligence forms the foundation for securing information and preserving customer relationships.
In the early days of air travel, baggage handling lacked the efficiency of modern systems. Imagine arriving after a long flight, only to find your carefully packed belongings lost in transit. This frustrating situation occurred routinely, creating challenges for both passengers and airline staff. Manual sorting processes and unreliable luggage tags contributed to frequent mishaps as air travel volumes increased.
Data Security and Breach Notification: A Critical Aspect

Data Security Best Practices
In our digital era, safeguarding information has become essential. Preventing unauthorized access to sensitive data through comprehensive protective measures represents a fundamental responsibility for all organizations. Effective strategies include complex authentication systems, layered security protocols, and consistent system maintenance. These precautions substantially decrease vulnerability to cyber threats while ensuring information remains accurate and accessible. Security failures can damage credibility, financial health, and client relationships.
Developing a thorough security framework serves as the initial requirement. Such policies should define proper data handling methods, categorization systems, and emergency procedures. Employee education programs also play a vital role. When staff members understand potential threats and reporting processes, they become active participants in maintaining security standards. Cultivating this awareness throughout an organization helps prevent incidents and reduces their potential consequences.
Breach Notification Requirements
Timely disclosure becomes imperative following security incidents. Adherence to legislation like GDPR and CCPA establishes necessary protocols for incident communication. Notification processes must include identifying impacted parties, describing the breach details, and providing assistance resources. Clear explanations about the event's nature, potential consequences, and corrective actions help maintain transparency. Open communication preserves stakeholder confidence during challenging situations.
Detailed records of incident investigations prove equally important. Documenting causes, effects, and remedial measures supports compliance efforts and future prevention. These archives serve as valuable references during subsequent reviews and help avoid repeating mistakes.
Responding to Data Security Breaches
Effective incident management requires predefined action plans. These procedures should address threat identification, containment measures, investigative processes, and recovery operations. Rapid, coordinated responses minimize operational disruption and preserve organizational reputation. Appropriate notification of relevant internal and external parties remains crucial throughout the process.
Cooperation with authorities, regulatory agencies, and security specialists enhances response effectiveness and prevents additional damage. External expertise often provides valuable perspectives for managing complex situations. Implementing system improvements and strengthened security measures following incidents helps prevent recurrence.

Read more about Data Privacy Regulations in EdTech: GDPR and Beyond
Hot Recommendations
- The Gamified Parent Teacher Conference: Engaging Stakeholders
- Gamification in Education: Making Learning Irresistibly Fun
- The Future of School Libraries: AI for Personalized Recommendations
- EdTech and the Future of Creative Industries
- Empowering Student Choice: The Core of Personalized Learning
- Building Community in a Hybrid Learning Setting
- VR for Special Education: Tailored Immersive Experiences
- Measuring the True Value of EdTech: Beyond Adoption Rates
- Addressing Digital Divide in AI Educational Access
- Preparing the Workforce for AI Integration in Their Careers